Translate this page into:
Double aortic arch: A rare case of dysphagia
* Corresponding author: Archit Dikshit, Department of Radiology, UN Mehta Institute of Cardiology and Research Centre, Civil hospital campus, Ahmedabad, India. architmdikshit@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Dikshit A, Patel S, Garachh M, Patel D, Deshpande S. Double aortic arch: A rare case of dysphagia. Future Health. 2024;2:94–96. doi: 10.25259/FH_8_2024
Abstract
Double aortic arch (DAA) is a rare cause of esophageal compression. We present a case of a seven-month-old male infant who presented with complaints of dysphagia and wheezing during crying. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) revealed a co-dominant double aortic arch forming a complete vascular ring around the trachea, causing its mild compression. Posteriorly, the aortic arch was seen, causing severe compression of the esophagus. The patient underwent double aortic arch repair and had an uneventful post-operative course, with resolution of the dysphagia.
Keywords
Double aortic arch
Vascular ring
Dysphagia
Double aortic arch (DAA) is a rare cause of esophageal compression. We present a case of a seven-month-old male infant, who presented to our institute with complaints of dysphagia and wheezing during crying. The patient was referred to the Radiology Department for computed tomography angiography (CTA) for further evaluation and to rule out any vascular cause of dysphagia. A co-dominant double aortic arch was noted, with bilateral common carotid and subclavian arteries originating from each arch [Figure 1]. The DAA was forming a complete vascular ring around the trachea, causing its mild compression [Figure 2]. Posteriorly, the aortic arch was seen, causing severe compression of the esophagus [Figure 3]. The patient underwent double aortic arch repair and had an uneventful postoperative course, with resolution of the dysphagia.
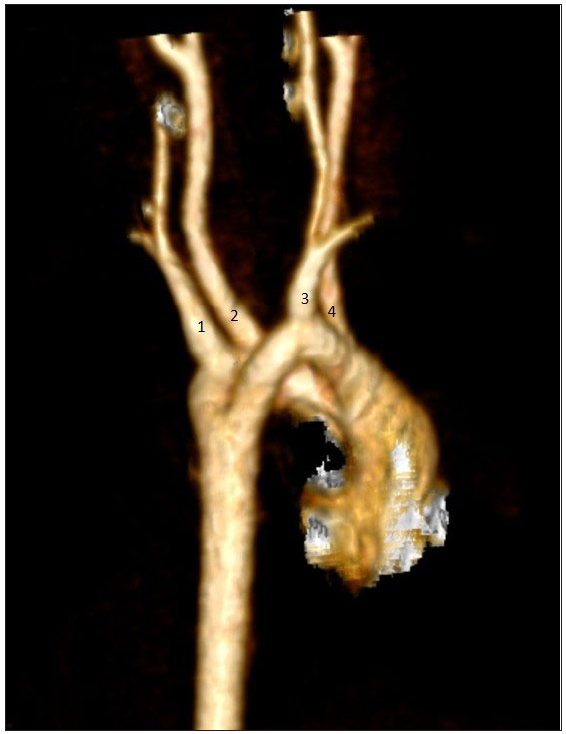
- Volume rendered image of computed tomography angiography (CTA) showing co-dominant double aortic arch. The right subclavian (1) and right common carotid (2) arteries are seen arising from the right aortic arch, while the left subclavian (3) and the left common carotid (4) arteries are seen arising from the left aortic arch.
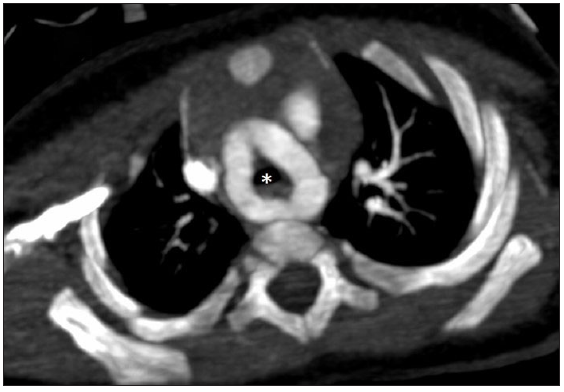
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA) axial oblique image showing the double aortic arch forming a complete ring around the trachea (white asterisk).
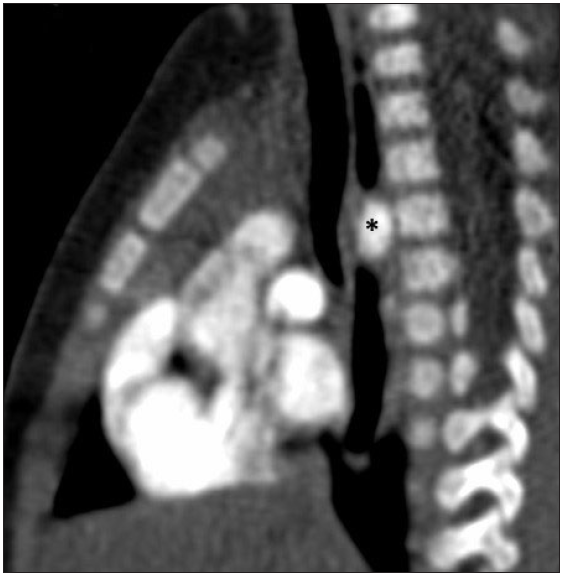
- Computed tomography angiography (CTA) sagittal image showing severe compression of the esophagus by the double aortic arch (black asterisk)
DAA is a relatively rare vascular ring that affects a small percentage of the population, with an incidence of approximately one in 15,000 births.1 During embryonic development, two aortic arches and two ductus arteriosus are formed. The regression of the dorsal segment of the right arch typically results in the formation of a single aortic arch. However, in some cases, both embryonic arches persist, which leads to a double aortic arch. It is noteworthy that the right arch is generally larger and higher than the left arch, and the descending aorta is opposite the dominant arch. The most common configuration includes a dominant right arch, a left-sided descending thoracic aorta, and a left-sided ligamentum arteriosum.2 It is also important to note that DAA with balanced anatomy is a relatively infrequent occurrence. During surgical thoracotomy and transection of the vascular ring, it is of utmost importance to determine the dominant side of the aortic arch.3 It is commonly found as an isolated anomaly but also has associations with other congenital heart disorders with the tetralogy of Fallot being the most commonly associated. 4 The presence of a double aortic arch in neonates and infants can present as respiratory distress, including wheezing, stridor, apneic episodes, persistent cough, and misdiagnosed asthma that is unresponsive to treatment, as well as persistent dysphagia due to compression of the trachea and esophagus.5
It is noteworthy that in DAA, bilateral common carotid and subclavian arteries originate from each arch. This results in a symmetrical appearance of the branch vessels on a transverse section just above the level of the arches, which is commonly referred to as the four-vessel or four-artery sign. This sign is crucial in differentiating an incomplete arch from the left brachiocephalic artery. Although it is not necessarily of diagnostic significance in all cases, it is an important sign to consider. In the case being discussed, the four-vessel sign was present, as evidenced by Figure 1.
All the patients will invariably need cross-sectional imaging for the diagnosis as well as pre-operative planning. At our institute, we prefer computed tomography angiography (CTA) for identifying vascular anomalies in infants. This is attributed to its ability to produce quick imaging results, minimize motion artifacts, and reduce the need for sedation, making it a safer option for young patients. However, it is important to note that CTA exposes patients to higher radiation levels, which can be mitigated through the use of low kilovolt potential, automatic tube current modulation, and adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction techniques. On the other hand, magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) is not an ideal option due to its limited availability, high cost, and requirement for sedation. However, MRA does not expose patients to ionizing radiation.
In conclusion, aortic arch anomalies, such as double aortic arch, are rare causes of tracheal compression and/or dysphagia in infants. However, clinicians should consider these vascular anomalies, and CT angiography is a valuable diagnostic tool for their detection.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
Patient’s consent not required as patients identity is not disclosed or compromised.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
References
- Congenital variants and anomalies of the aortic arch. Radio Graphics. 2017;37:32-51.
- [Google Scholar]
- Vascular rings: A practical approach to imaging diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol. 2005;35:961-79.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trends in vascular ring surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:1339-47.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rare causes of persistent wheeze that mimic poorly controlled asthma. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2013201100.
- [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central] [Google Scholar]








